Yeast allergy is a common issue, and it affects people all over the world. This article will give a complete overview of yeast allergy, its causes, symptoms, and treatment. Through the discussion of the different triggers and presentations of this allergy, readers will have useful information on how to manage and avoid allergic reactions. In addition, the article will analyze available treatments ranging from diet changes to medicine, educating readers on what is required to beat yeast allergies effectively and live their best life.
Introduction
Yeast allergy is an abnormal immune reaction to yeast, a type of fungus used in food production and baking. Yeast allergy can produce symptoms varying from mild inconvenience to severe reactions. Understanding yeast allergy is crucial for individuals who experience reactions to foods that have yeast, as it will allow them to identify and manage their condition. In this article, we will be discussing the causes, symptoms, and treatment of yeast allergy, providing helpful information on this more prevalent condition.
Causes of Yeast Allergy
Yeast allergy occurs when the immune system mistakenly recognizes yeast as a foreign agent and mounts an allergic reaction. The immune system produces antibodies called immunoglobulin E (IgE) in response to yeast, which releases histamine and other chemicals that cause the symptoms of an allergy.
Common causes of yeast allergies
Baker’s yeast: Saccharomyces cerevisiae, also referred to as baker’s yeast, is one of the common causes of yeast allergy. Baker’s yeast is used in bread baking, beer brewing, and wine fermentation.
Brewer’s yeast: Saccharomyces cerevisiae, another type of yeast, is used in beer brewing and health supplements. Brewer’s yeast can also be an allergen in some people.
Candida: Candida is a yeast that is normally found in the human body, notably in the gastrointestinal tract. A Candida overgrowth may result in yeast infection and potentially in allergic reactions.
Foods: Certain foods contain yeast or are fermented with yeast, which may induce allergic reactions. They are bread, pastry, beer, wine, vinegar, soy sauce, and cheese.
Risk factors for developing a yeast allergy
Family history: People with a family history of allergies, including yeast allergy, are more likely to develop a yeast allergy. Genetic factors control the susceptibility of an individual to allergies.
Weakened immune system: Patients with weakened immune systems, i.e., those who have HIV/AIDS, are undergoing chemotherapy, or on immunosuppressant drugs, are more likely to develop yeast allergies.
History of other allergies: Individuals with a history of other allergies, such as pollen or mold allergy, are more susceptible to developing a yeast allergy.
Excessive exposure to yeast: Excessive exposure to yeast over a long duration of time, either due to occupational exposure or frequent consumption of yeast-containing foods, may increase the risk of developing a yeast allergy.
Understanding the causes of yeast allergy is crucial in knowing triggers and managing symptoms accordingly. Through avoiding exposure and proper treatment, yeast allergy patients can minimize this condition’s impact on their lives.
Symptoms of Yeast Allergy
Yeast allergies can be experienced through a range of symptoms that are felt in various parts of the body. These symptoms can range from mild to severe and can vary from person to person. It needs to be noted that yeast allergies are different from yeast infections, which are caused by an overgrowth of yeast in the body. In this article, we will be describing the common symptoms of yeast allergies, including physical, digestive, respiratory, and skin symptoms.
Physical symptoms
Yeast allergy may also lead to a range of physical symptoms that may include:
– Fatigue and weakness: Individuals with yeast allergy are likely to suffer from chronic fatigue and overall weakness.
– Headaches: Recurring headaches or migraines may be experienced by some individuals as a result of a yeast allergy.
– Joint and muscle pain: Yeast allergy may lead to joint pain and muscle pain, causing stiffness and pain.
– Swelling and inflammation: Allergic reactions to yeast cause swelling and inflammation in the body, such as the face, hands, or feet.
Digestive symptoms
Yeast allergy also affects the digestive system and causes the following symptoms:
– Abdominal cramps or pain: Individuals with yeast allergy experience abdominal pain or cramping.
– Gas and bloating: Yeast allergy causes excessive gas and bloating and is uncomfortable.
– Diarrhea or constipation: Some people may experience diarrhea or constipation as a result of yeast allergy.
– Nausea and vomiting: In some people, yeast allergy leads to nausea and vomiting.
Symptoms in the respiratory system
Yeast allergy affects the respiratory system, resulting in the following symptoms:
– Sneezing and nasal congestion: There is constant sneezing and nasal congestion in people who have yeast allergies.
– Wheezing and coughing: Allergies to yeast may cause wheezing and coughing incessantly.
– Breathlessness: Some other people may have shortness of breath or breathlessness due to an allergy towards yeast.
– Sinusitis: Allergy to yeast can result in chronic sinusitis, resulting in inflammation and congestion of the sinuses.
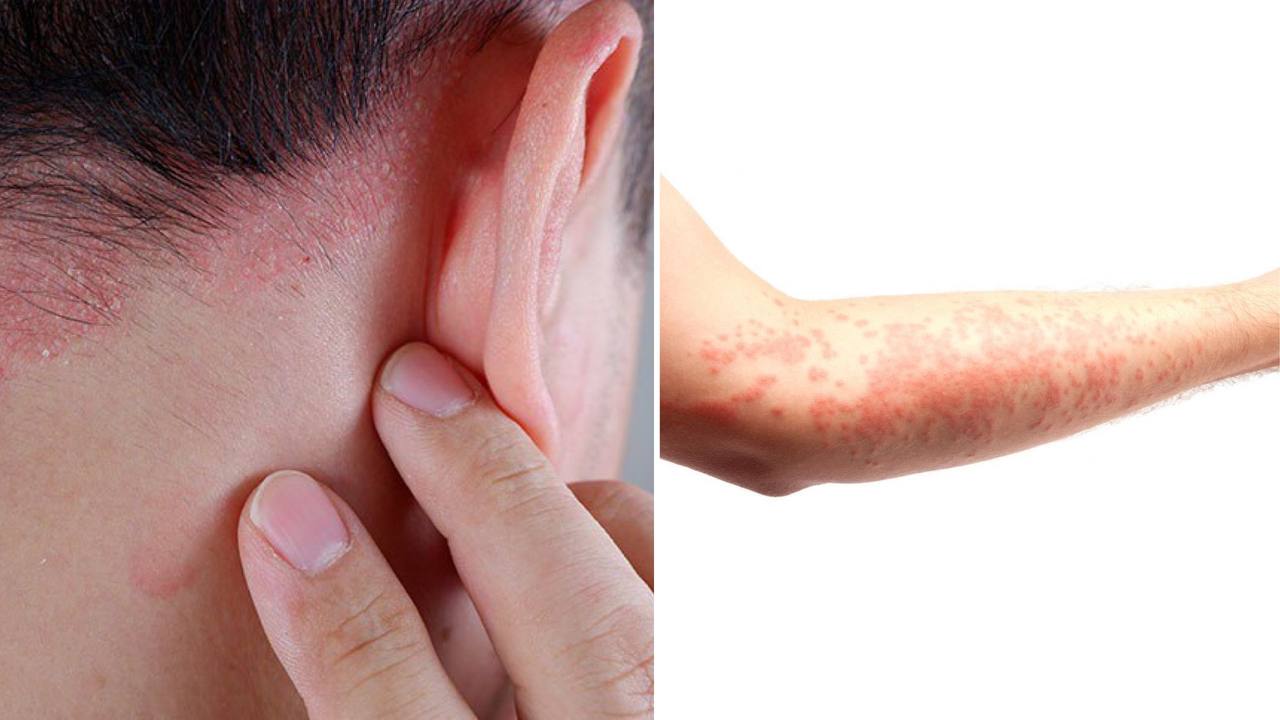
Skin symptoms
Allergies to yeast can also occur in the form of various skin symptoms, including:
– Itching skin: Individuals with yeast allergies may experience itchy skin that lasts, accompanied by redness as well.
– Hives and rashes: Rashes and hives on the skin can be caused by yeast allergy.
– Eczema flares: A yeast allergy can cause or exacerbate eczema, leading to flare-ups and irritation on the skin.
– Dermatitis: Others get dermatitis, where the skin becomes inflamed and irritated due to a yeast allergy.
It is advisable to visit a doctor for proper diagnosis in case of an allergy to yeast. They can determine the cause of your condition and recommend suitable treatment measures.
Treatment of Yeast Allergy
Avoiding food and products with yeast
The initial and foremost method of treating yeast allergy is to avoid food and products with yeast. This involves thoroughly reading food packaging and ingredient listings to identify any yeast-based foods such as baker’s yeast, brewer’s yeast, or yeast extract. One also must avoid naturally yeast-containing foods such as bread, beer, and fermented foods. Additionally, yeast-allergic patients must be aware of cross-contamination because yeast is present in foods processed in plants that process yeast-containing products.
Medications for symptom relief
In some cases, drugs are prescribed or recommended to treat symptoms of yeast allergy. Antihistamines help to relieve itching, sneezing, and other allergic signs caused by yeast. Nasal corticosteroids may be prescribed to eliminate nasal congestion and inflammation. Topical corticosteroids are used to eliminate skin symptoms such as rashes and itching. A doctor needs to be consulted before taking any drug to avoid misuse and appropriate dosage.
Allergy testing and treatment options
For individuals with acute or chronic yeast allergy symptoms, allergists may recommend testing for an allergy in order to determine what specific allergens precipitate the symptoms of an allergy. The patient may have either a skin test or a blood test to check for the presence of yeast-specific IgE antibodies. Depending on test outcomes, there are several options for desensitization treatment, such as shots or sublingual immunotherapy. Both involve exposing the immune system to yeast allergens over a period of time and thus reduce allergy symptoms.
Lifestyle changes for managing yeast allergy
Certain lifestyle changes can also manage yeast allergies. Proper personal hygiene, e.g., frequent hand washing and cleanliness of residences, might minimize exposure to yeast. Fragrance-free and hypoallergenic personal care products should also be used to avoid skin reactions. Avoiding areas with high yeast content, e.g., damp or moldy places, might also be helpful. In addition, stress control and a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can also enhance overall immunity and potentially reduce the severity of allergic reactions.